If your Wi-Fi started dropping after installing Windows 11 25H2, you’re in the right place. This guide Fixlp walks you through reliable, practical fixes — from quick checks to deeper driver and network resets — plus exact places to add step-by-step screenshots so readers (and Google) love the post.
Below you’ll find clear steps, what each step does, and when to escalate (rollback or contact support). I’ve also included recommended places to insert screenshots — add them to match each step to increase user trust and search visibility.
Quick overview — what’s likely happening
Feature updates like 25H2 can change drivers, power settings or network stack behavior, which sometimes causes Wi-Fi instability on certain machines. Microsoft’s own guidance recommends running the built-in network troubleshooter and using Network Reset for stubborn cases.
If you want the short checklist before diving into steps: restart router & PC, forget/reconnect the network, update/roll back drivers, disable Wi-Fi adapter power saving, reset the network stack, then consider uninstalling the update if the issue persists. Detailed steps below.
Before you start (two quick checks)
Confirm the problem: does wired Ethernet work consistently? If yes, the issue is almost certainly Wi-Fi-specific (adapter/driver/config).
Try a different network (phone hotspot). If the laptop stays connected to another network, the router or specific band/settings may be involved.
If both checks point toward Windows, continue with the steps below.
Step 1 — Basic restart & forget (fast wins)
Restart your PC and router/modem. Simple restarts fix transient problems.
On Windows: Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi > Manage known networks. Select your SSID and choose Forget. Then reconnect using the password.

Why: This clears cached network profiles and forces Windows to negotiate fresh settings with your router. Many users see an immediate fix.
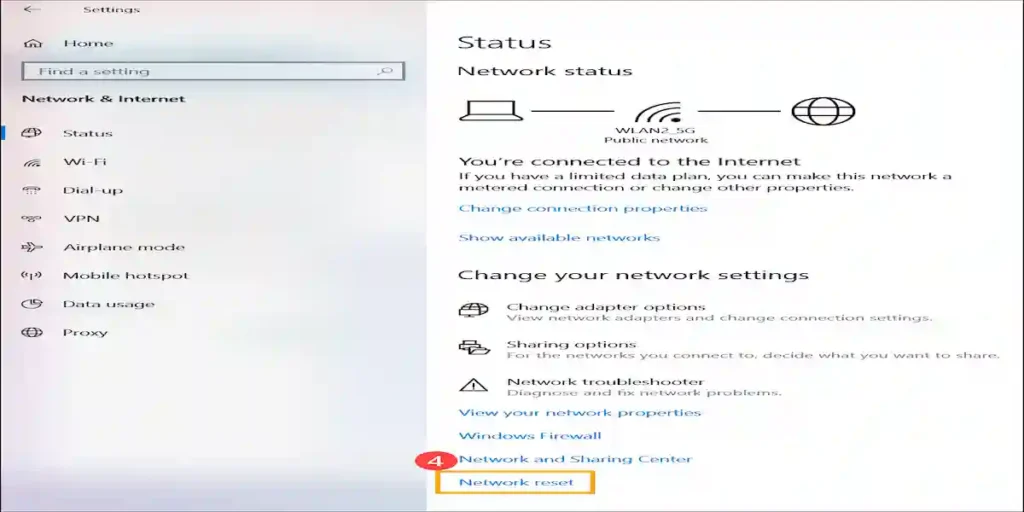
Step 2 — Run Windows’ network troubleshooter and Network Reset (Microsoft recommended)
Open Settings > System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters and run Network Adapter. If that doesn’t fix it, go to Settings > Network & Internet > Advanced network settings > Network reset and click Reset now. Windows will restart and reinstall network adapters.
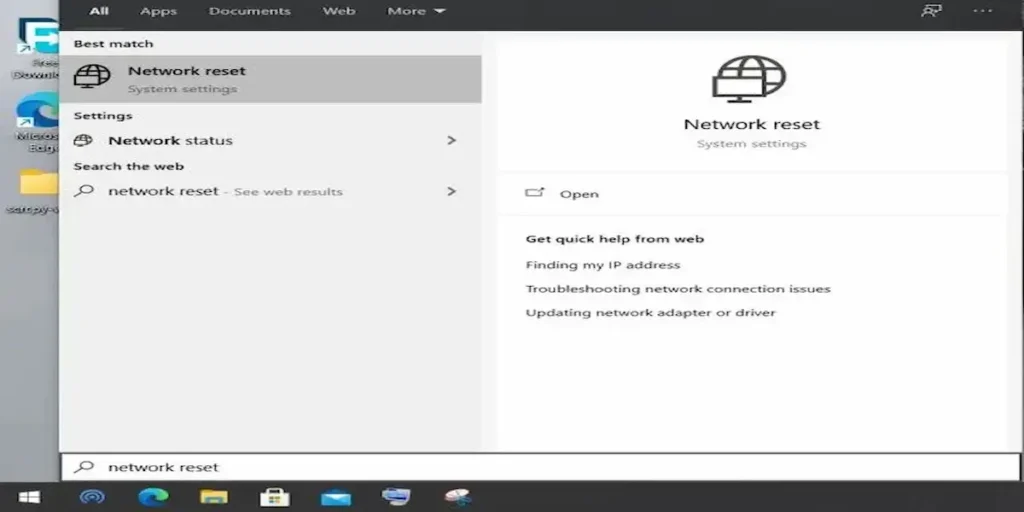
Why: The Network Reset clears complex misconfigurations and is the official first-line remedy Microsoft provides when connectivity is unstable.
Step 3 — Update, rollback, or reinstall the Wi-Fi driver
Open Device Manager > Network adapters. Right-click your wireless adapter → Properties → Driver.
If Roll Back Driver is available, try it (useful if the update installed a bad driver). If not, choose Update Driver → Search automatically or download the exact driver from your PC/laptop maker or the Wi-Fi adapter vendor (Intel, Realtek, Broadcom, MediaTek).
If updates and rollbacks don’t help, choose Uninstall device, check Delete the driver software for this device (if present), then Scan for hardware changes to let Windows reinstall a fresh driver.
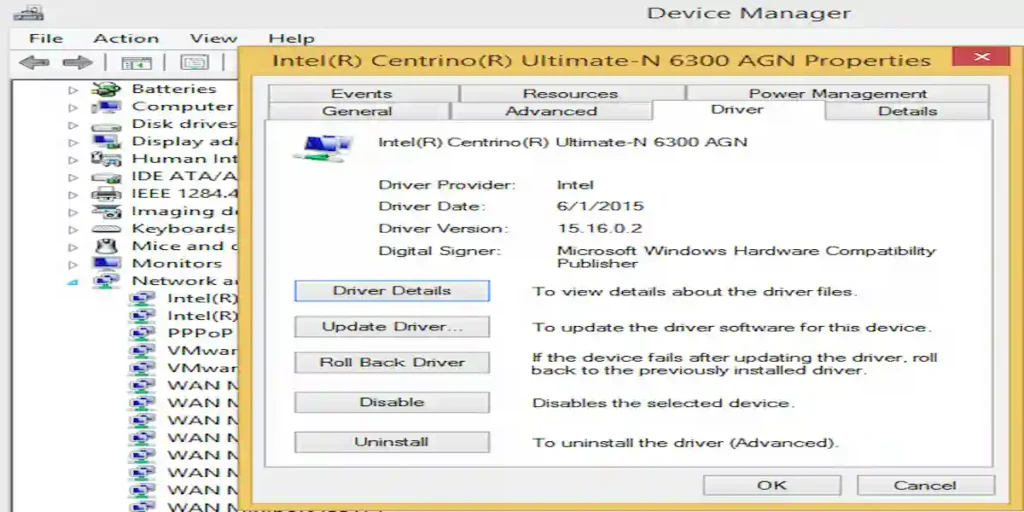
Why: Windows updates can replace drivers with incompatible versions. Rolling back or reinstalling a vendor’s official driver often fixes persistent disconnects.
Step 4 — Disable adapter power saving (common culprit)
Open Device Manager > Network adapters, right-click the adapter → Properties > Power Management and uncheck Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power. Also set the wireless adapter to Maximum Performance in Power Options (Control Panel > Power Options > Change plan settings > Change advanced power settings > Wireless Adapter Settings > Power Saving Mode).
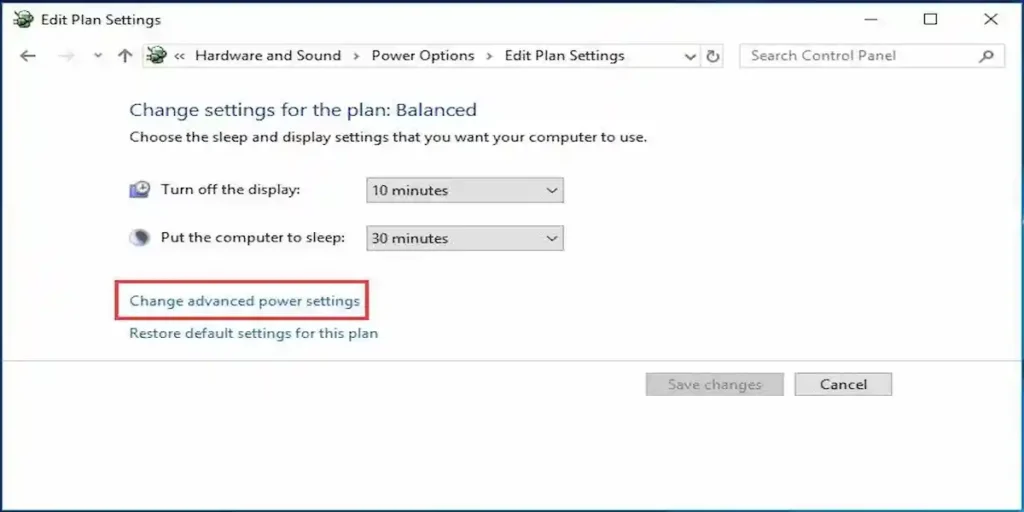
Why: Windows can turn off the Wi-Fi adapter to conserve power; disabling this often eliminates timed disconnects. Microsoft documents how to change these settings.
Step 5 — Reset the network stack (commands)
Open an elevated Command Prompt (run as administrator) and run these commands one by one (press Enter after each):
netsh winsock reset
netsh int ip reset
ipconfig /release
ipconfig /renew
ipconfig /flushdns
After these, restart your PC. These commands reset the core Windows network components and clear stale entries. Community reports and Microsoft forum answers frequently list these as effective fixes.
Step 6 — Temporary workarounds while a permanent fix is pending
If the fixes above don’t help and the issue appeared right after 25H2, try these short-term backups:
Plug an Ethernet cable for critical work.
Use a USB Wi-Fi adapter (commonly fixes driver-compatibility problems).
Switch your router to 2.4GHz (if the adapter struggles on 5GHz) or change router channel and disable Wi-Fi 6/6E temporarily. Community threads show users getting stable connections after falling back to different bands or disabling advanced router features.

Step 7 — If many users are affected: consider rolling back 25H2 (use cautiously)
If your troubleshooting points to 25H2 as the cause (multiple machines, confirmed by forums or enterprise support), you can uninstall the feature update: Settings > Windows Update > Update history > Uninstall updates. Microsoft provides official guidance on removing updates; for full rollbacks you may also use Recovery > Go back to the previous version (only available for a limited time after upgrade). Always back up data first.
Why this matters: Rolling back is a last resort. Use it if you verified the update introduced the problem and other fixes fail.
When to escalate — what to tell support
If you contact Microsoft support or your PC maker, provide:
Windows build & version (Settings > System > About)
Exact behavior (disconnects every X minutes, reconnects automatically or not)
Actions already taken (driver rollback, netsh, network reset)
Event Viewer logs around the time of a disconnect — look for WLAN-AutoConfig or Network Adapter error events.
Providing precise steps you’ve already tried speeds troubleshooting.
Final notes & monitoring
Keep an eye on Microsoft’s Windows release health and update notes. If 25H2 introduces a known bug, Microsoft usually posts workarounds and a timeline for fixes. Check the Windows Message Center and release health dashboard.
Add a “Last updated” date to your article and update it when Microsoft releases a patch. Freshness matters for ranking when an issue is update-specific.
FAQ
Can I uninstall 25H2 in case my Wi-Fi fails?
You can uninstall the updates from Settings > Update history > Uninstall updates, but do this only if you have tried everything else and are sure that this update is causing the problem. But remember to take backup of all your important files before that!
Are the netsh commands safe?
Yes- those commands reset the Windows networking components and are considered safe steps in troubleshooting. After the reset, you will need to connect to Wi-Fi again.